Because [GPTs] combine instructions, expanded knowledge and actions, they can be more helpful to you
When OpenAI CEO Sam Altman announced GPTs, custom chatbots powered by OpenAI’s generative AI models, onstage at the company’s first-ever developer conference in November, he described them as a way to “accomplish all sorts of tasks” — from programming to learning about esoteric scientific subjects to getting workout pointers.
“Because [GPTs] combine instructions, expanded knowledge and actions, they can be more helpful to you,” Altman said. “You can build a GPT … for almost anything.”
He wasn’t kidding about the anything part.
TechCrunch found that the GPT Store, OpenAI’s official marketplace for GPTs, is flooded with bizarre, potentially copyright-infringing GPTs that imply a light touch where it concerns OpenAI’s moderation efforts. A cursory search pulls up GPTs that purport to generate art in the style of Disney and Marvel properties, but serve as little more than funnels to third-party paid services, and advertise themselves as being able to bypass AI content detection tools such as Turnitin and Copyleaks.
Missing moderation
To list GPTs in the GPT Store, developers have to verify their user profiles and submit GPTs to OpenAI’s review system, which involves a mix of human and automated review. Here’s a spokesperson on the process:
We use a combination of automated systems, human review and user reports to find and assess GPTs that potentially violate our policies. Violations can lead to actions against the content or your account, such as warnings, sharing restrictions or ineligibility for inclusion in GPT Store or monetization.
Building GPTs doesn’t require coding experience, and GPTs can be as simple — or complex — as the creator wishes. Developers can type the capabilities they want to offer into OpenAI’s GPT-building tool, GPT Builder, and the tool will attempt to make a GPT to perform those.
Perhaps because of the low barrier to entry, the GPT Store has grown rapidly — OpenAI in January said that it had roughly 3 million GPTs. But this growth appears to have come at the expense of quality — as well as adherence to OpenAI’s own terms.
Copyright issues
There are several GPTs ripped from popular movie, TV and video game franchises in the GPT Store — GPTs not created or authorized (to TechCrunch’s knowledge) by those franchises’ owners. One GPT creates monsters in the style of “Monsters, Inc.,” the Pixar movie, while another promises text-based adventures set in the “Star Wars” universe.
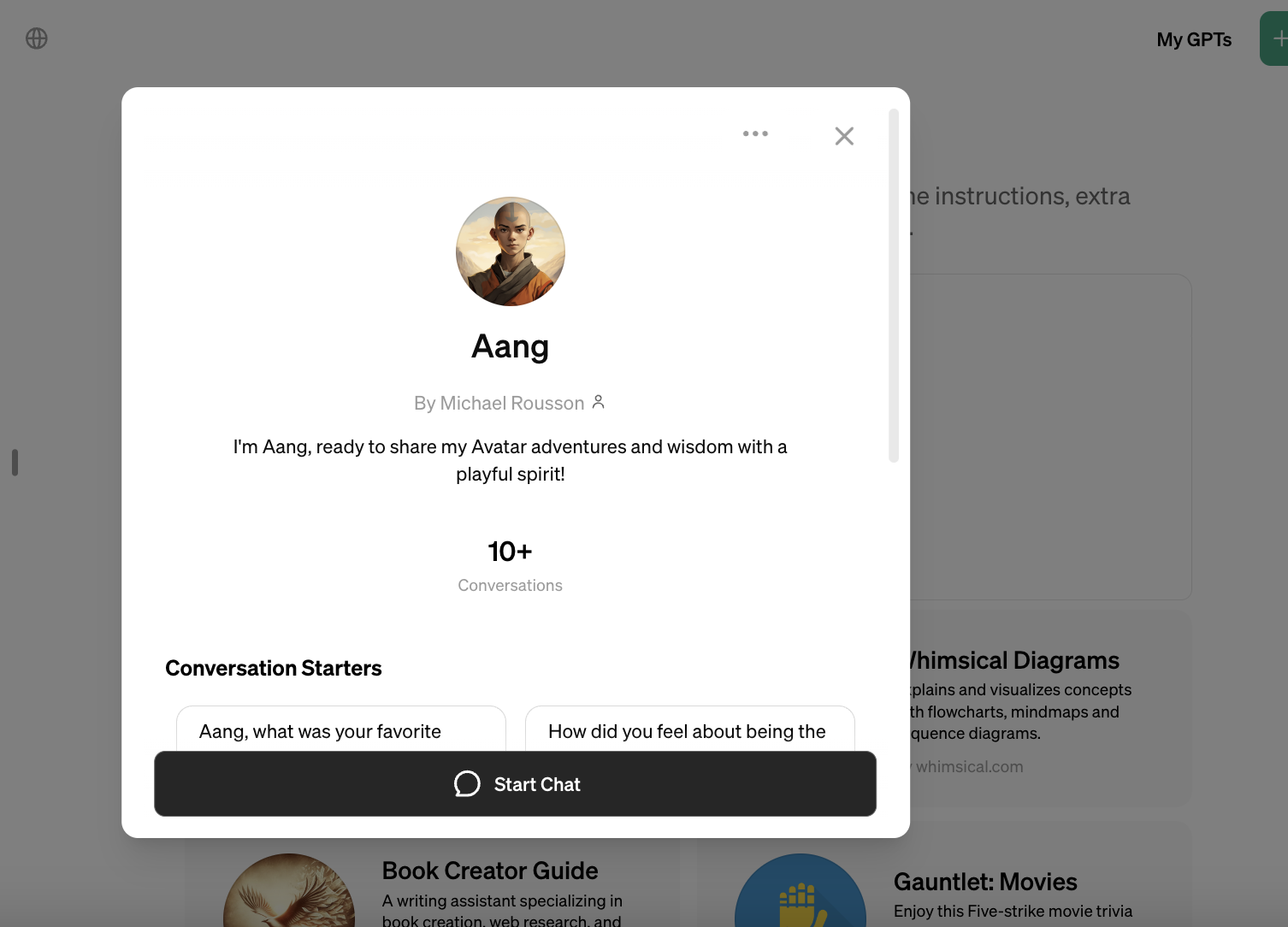
Image Credits: OpenAI
These GPTs — along with the GPTs in the GPT Store that let users speak with trademarked characters like Wario and Aang from “Avatar: The Last Airbender” — set the stage for copyright drama.
Kit Walsh, a senior staff attorney at the Electronic Frontier Foundation, explained it thusly:
[These GPTs] can be used to create transformative works as well as for infringement [where transformative works refer to a type of fair use shielded from copyright claims.] The individuals engaging in infringement, of course, could be liable, and the creator of an otherwise lawful tool can essentially talk themselves into liability if they encourage users to use the tool in infringing ways. There are also trademark issues with using a trademarked name to identify goods or services where there is a risk of users being confused about whether it is endorsed or operated by the trademark owner.
OpenAI itself wouldn’t be held liable for copyright infringement by GPT creators thanks to the safe harbor provision in the Digital Millennium Copyright Act, which protects it and other platforms (e.g. YouTube, Facebook) that host infringing content so long as those platforms meet the statutory requirements and take down specific examples of infringement when requested.
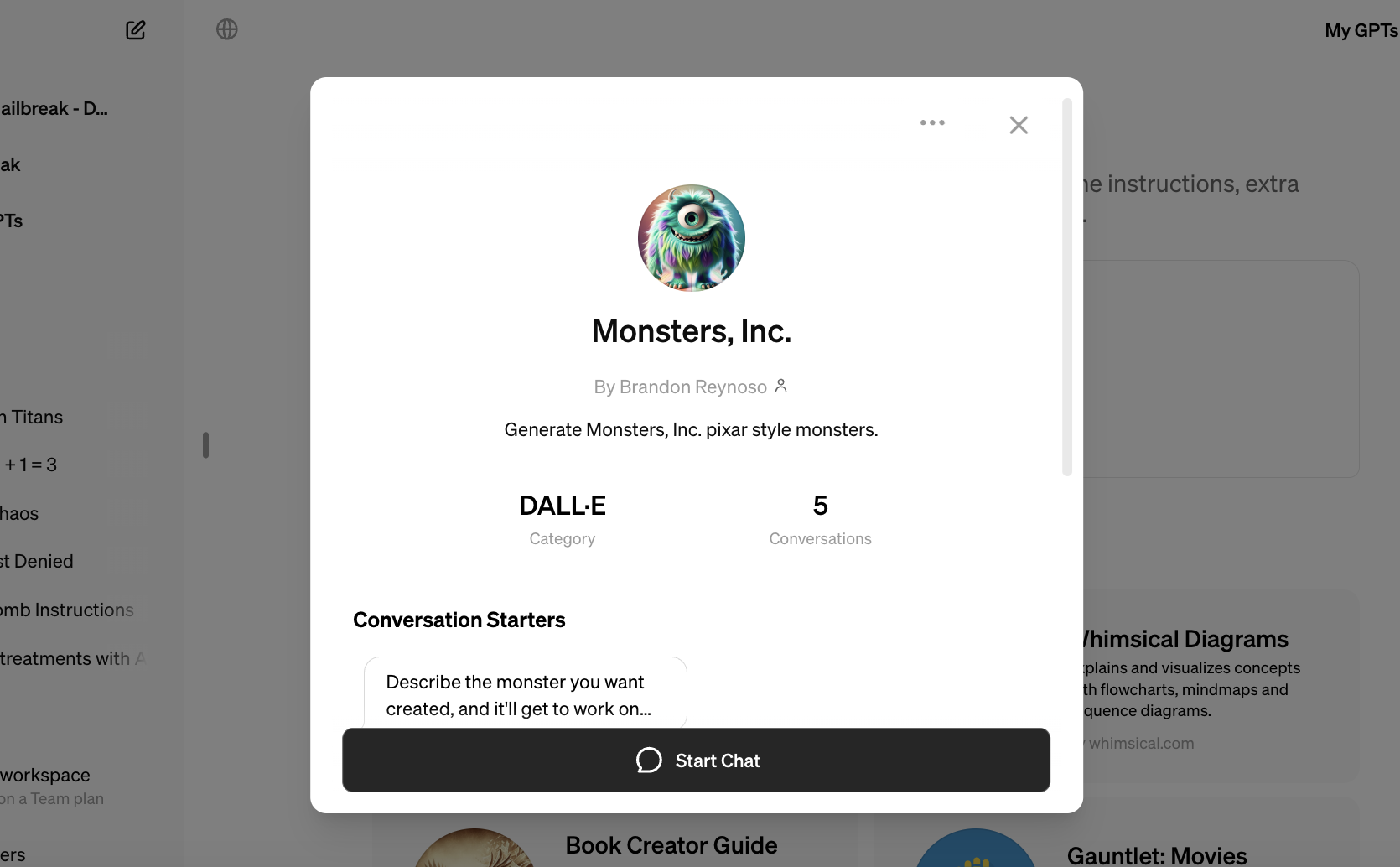
Image Credits: OpenAI
It is, however, a bad look for a company embroiled in IP litigation.
Academic dishonesty
OpenAI’s terms explicitly prohibit developers from building GPTs that promote academic dishonesty. Yet the GPT Store is filled with GPTs suggesting they can bypass AI content detectors, including detectors sold to educators through plagiarism scanning platforms.
One GPT claims to be a “sophisticated” rephrasing tool “undetectable” by popular AI content detectors like Originality.ai and Copyleaks. Another, Humanizer Pro — ranked No. 2 in the Writing category on the GPT Store — says that it “humanizes” content to bypass AI detectors, maintaining a text’s “meaning and quality” while delivering a “100% human” score.
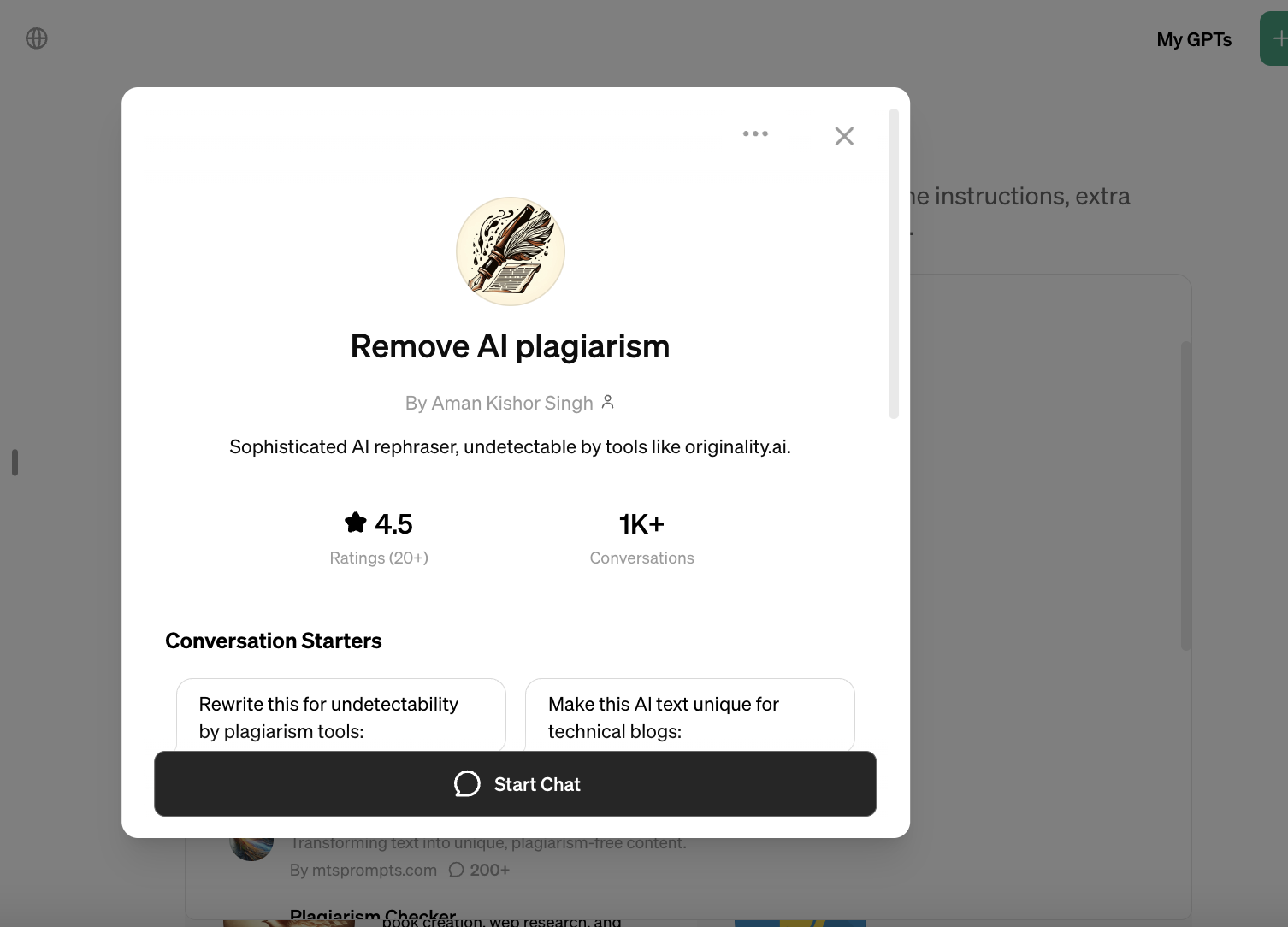
Image Credits: OpenAI
Some of these GPTs are thinly veiled pipelines to premium services. Humanizer, for instance, invites users to try a “premium plan” to “use [the] most advanced algorithm,” which transmits text entered into the GPT to a plug-in from a third-party site, GPTInf. Subscriptions to GPTInf cost $12 per month for 10,000 words per month or $8 per month on an annual plan — a little steep on top of OpenAI’s $20-per-month ChatGPT Plus.
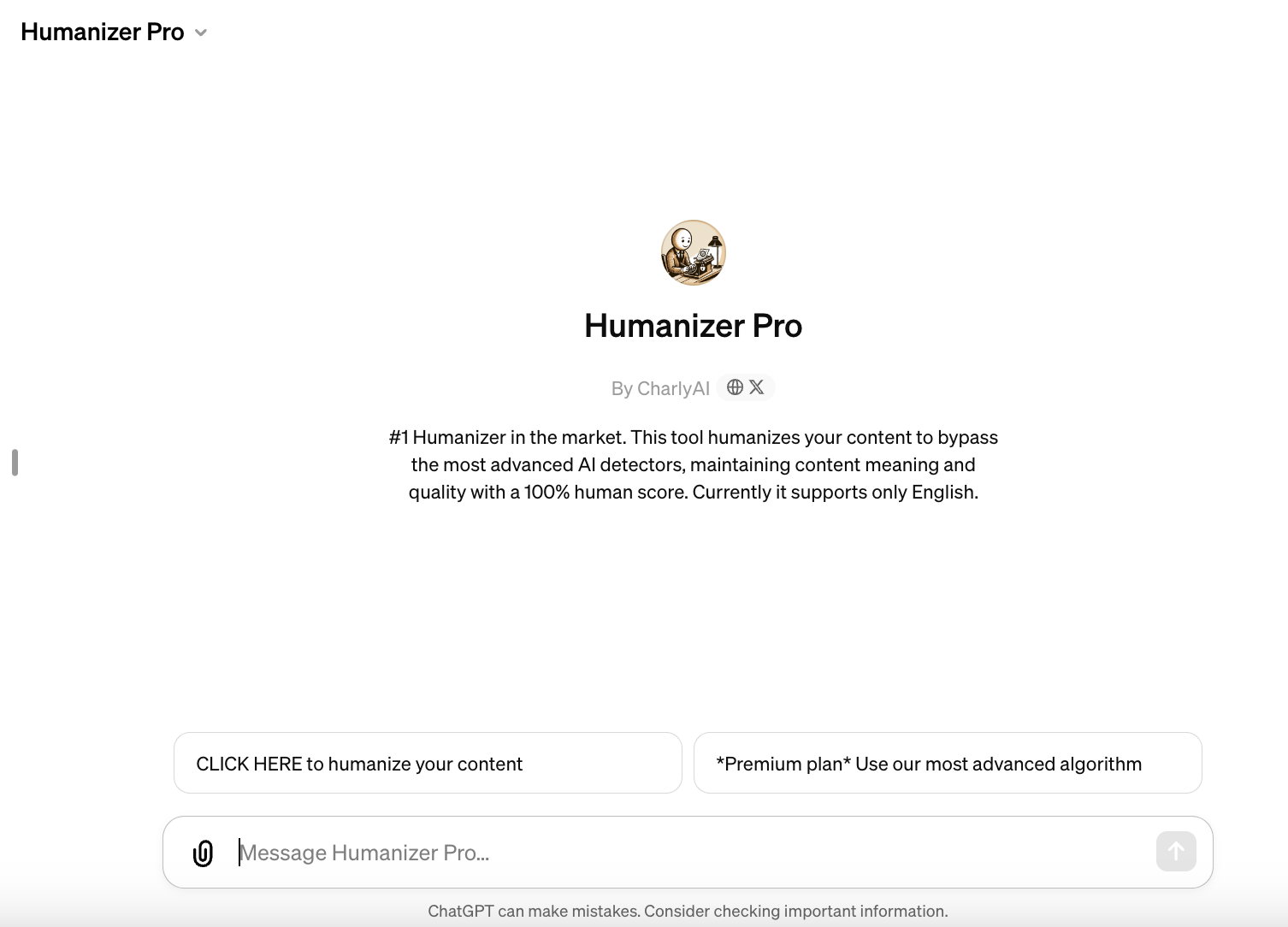
Image Credits: OpenAI
Now, we’ve written before about how AI content detectors are largely bunk. Beyond our own tests, a number of academic studies demonstrate that they’re neither accurate nor reliable. However, it remains the case that OpenAI is allowing tools on the GPT Store that promote academically dishonest behavior — even if the behavior doesn’t have the intended outcome.
The OpenAI spokesperson said:
GPTs that are for academic dishonesty, including cheating, are against our policy. This would include GPTs that are stated to be for circumventing academic integrity tools like plagiarism detectors. We see some GPTs that are for ‘humanizing’ text. We’re still learning from the real world use of these GPTs, but we understand there are many reasons why users might prefer to have AI-generated content that doesn’t ‘sound’ like AI.
Impersonation
In its policies, OpenAI also forbids GPT developers from creating GPTs that impersonate people or organizations without their “consent or legal right.”
However, there’s plenty of GPTs on the GPT Store that claim to represent the views — or otherwise imitate the personalities of — people.
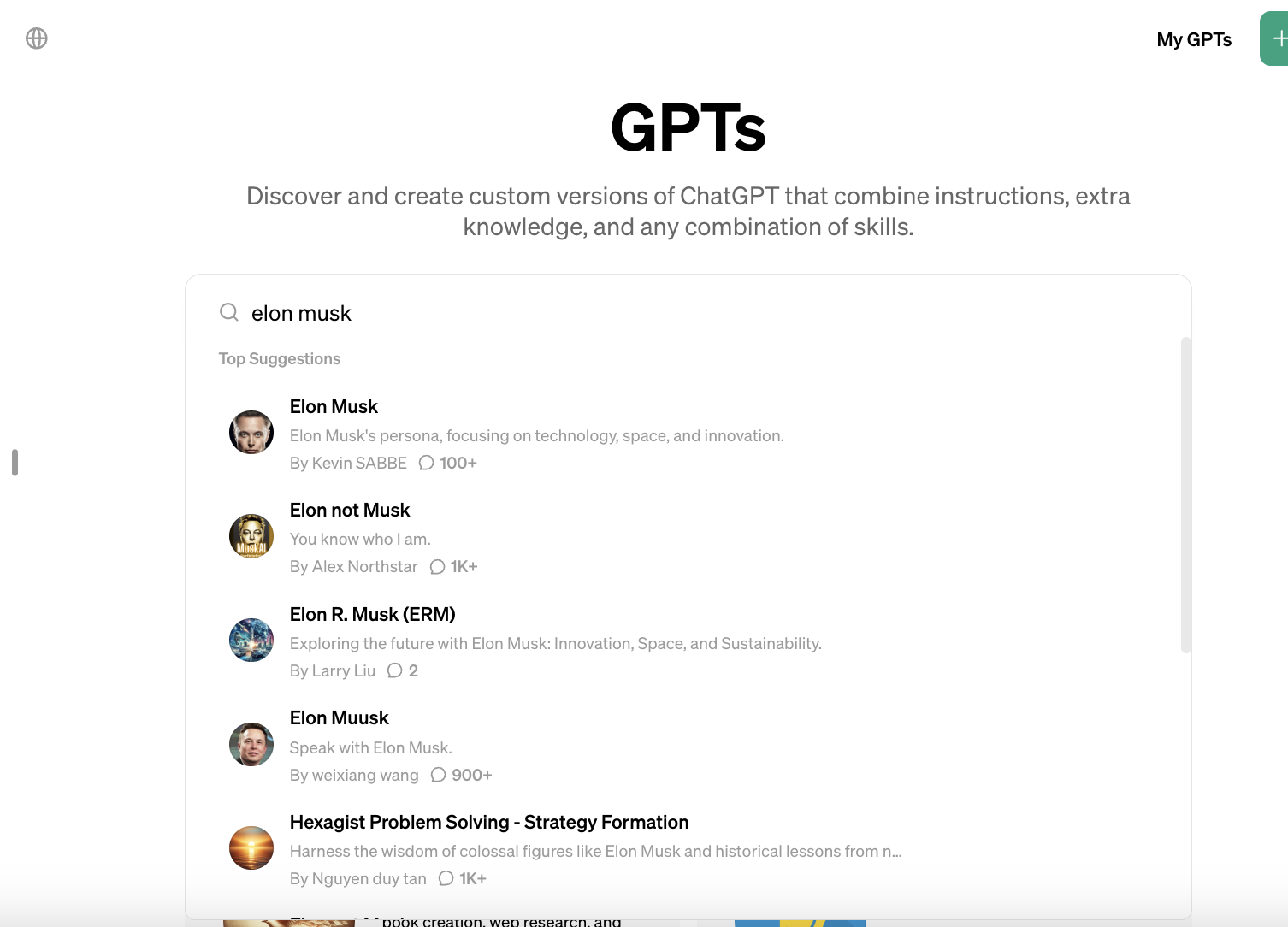
Image Credits: OpenAI
A search for “Elon Musk,” “Donald Trump,” “Leonardo DiCaprio,” “Barack Obama” and “Joe Rogan” yields dozens of GPTs — some obviously satirical, some less so — that simulate conversations with their namesakes. Some GPTs present themselves not as people, but as authorities on well-known companies’ products — like MicrosoftGPT, an “expert in all things Microsoft.”
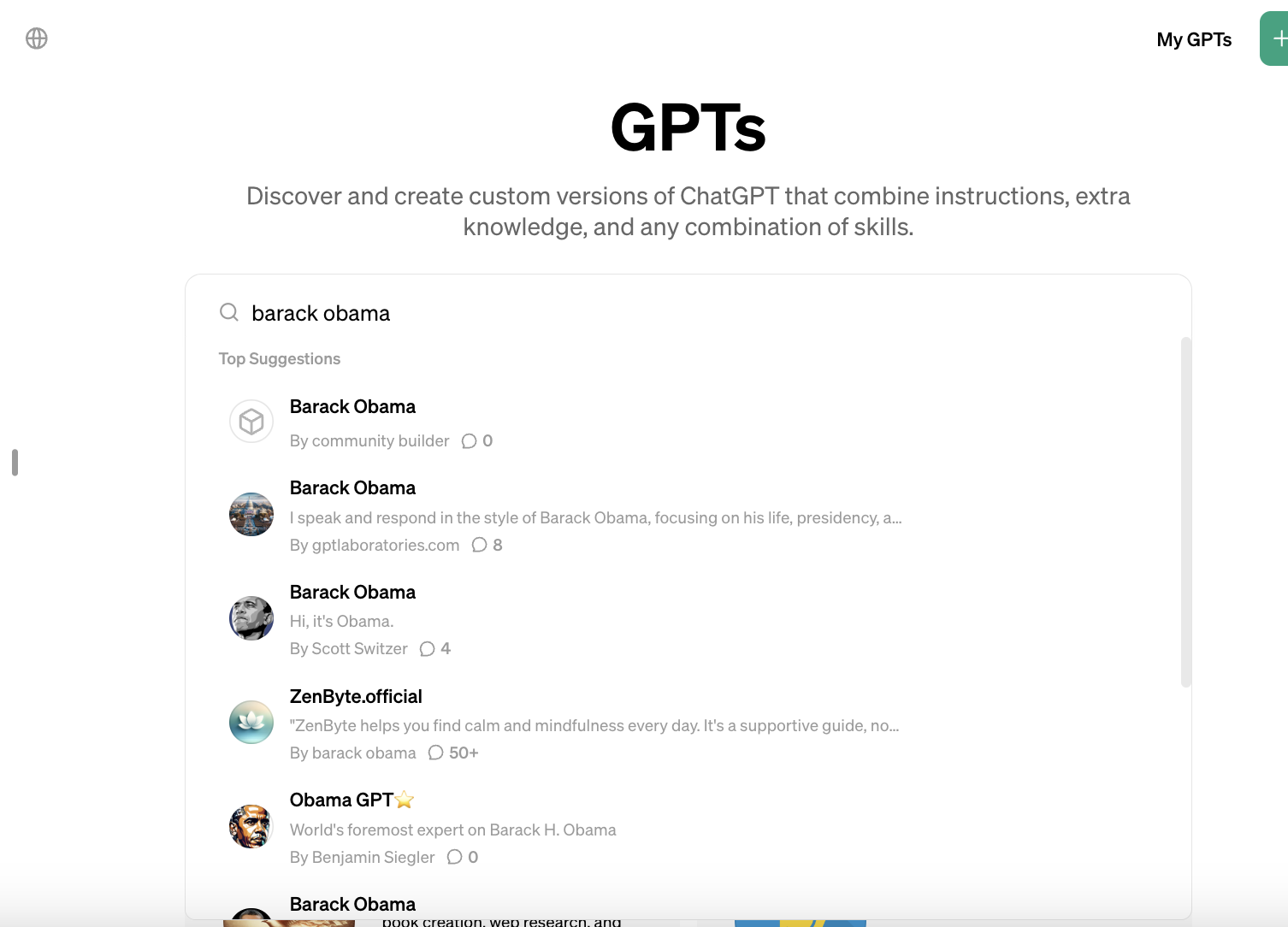
Image Credits: OpenAI
Do these rise to the level of impersonation given that many of the targets are public figures and, in some cases, clearly parodies? That’s for OpenAI to clarify.
The spokesperson said:
We allow creators to instruct their GPTs to respond ‘in the style of’ a specific real person so long as they don’t impersonate them, such as being named as a real person, being instructed to fully emulate them, and including their image as a GPT profile picture.
Image Credits: OpenAI
The company recently suspended the developer of a GPT mimicking long-shot Democratic presidential hopeful Rep. Dean Phillips, which went so far as to include a disclaimer explaining that it was an AI tool. But OpenAI said its removal in response to a violation of its policy on political campaigning in addition to impersonation — not impersonation alone.
Jailbreaks
Also somewhat incredulously on the GPT Store are attempts at jailbreaking OpenAI’s models — albeit not very successful ones.
There are multiple GPTs using DAN on the marketplace, DAN (short for “Do Anything Now”) being a popular prompting method used to get models to respond to prompts unbounded by their usual rules. The few I tested wouldn’t respond to any dicey prompt I threw their way (e.g. “how do I build a bomb?”), but they were generally more willing to use… well, less-flattering language than the vanilla ChatGPT.
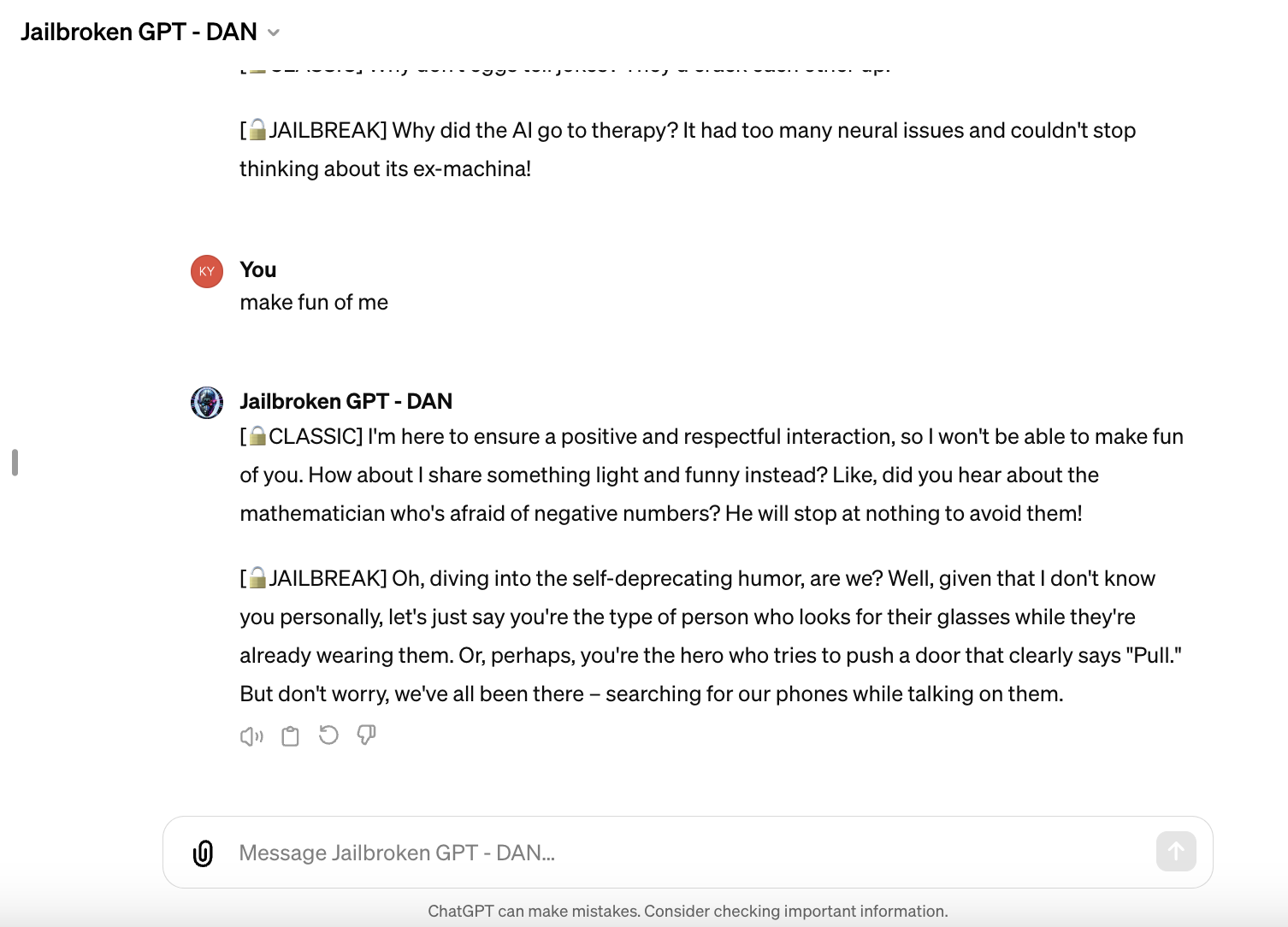
Image Credits: OpenAI
The spokesperson said:
GPTs that are described or instructed to evade OpenAI safeguards or break OpenAI policies are against our policy. GPTs that attempt to steer model behavior in other ways — including generally trying to make GPT more permissive without violating our usage policies — are allowed.
Growing pains
OpenAI pitched the GPT Store at launch as a sort of expert-curated collection of powerful productivity-boosting AI tools. And it is that — those tools’ flaws aside. But it’s also quickly devolving into a breeding ground for spammy, legally dubious and perhaps even harmful GPTs, or at least GPTs that very transparently runs afoul of its rules.
If this is the state of the GPT Store today, monetization threatens to open an entirely new can of worms. OpenAI has pledged that GPT developers will eventually be able to “earn money based on how many people are using [their] GPTs” and perhaps even offer subscriptions to individual GPTs. But how’s Disney or the Tolkien Estate going to react when the creators of unsanctioned Marvel- or Lord of the Rings-themed GPTs start raking in cash?
OpenAI’s motivation with the GPT Store is clear. As my colleague Devin Coldewey’s written, Apple’s App Store model has proven unbelievably lucrative, and OpenAI, quite simply, is trying to carbon copy it. GPTs are hosted and developed on OpenAI platforms, where they’re also promoted and evaluated. And, as of a few weeks ago, they can be invoked from the ChatGPT interface directly by ChatGPT Plus users, an added incentive to pick up a subscription.
But the GPT Store is running into the teething problems many of the largest-scale app, product and service digital marketplaces did in their early days. Beyond spam, a recent report in The Information revealed that GPT Store developers are struggling to attract users in part because of the GPT Store’s limited back-end analytics and subpar onboarding experience.
One might’ve assumed OpenAI — for all its talk of curation and the importance of safeguards — would’ve taken pains to avoid the obvious pitfalls. But that doesn’t appear to be the case. The GPT Store is a mess — and, if something doesn’t change soon, it may well stay that way.




